Amino acids in polypeptides
Charged polar side chains
Amino acids with charged (basic or acidic) side chains are very polar and they are nearly always found in the outside of protein molecules.
- Acidic side chains
Carboxyl groups in water loose an H+ ion to become negatively charged.
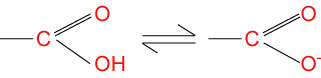
They are therefore acid.
Amino acids with acidic side chains:
- Aspartic, Asp, D
- Glutamic, Glu, E
- Basic side chains
Amines in water combine with an H+ ion to become positively charged
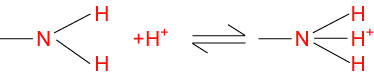
They are therefore basic.
Amino acids with basic side chains:
- Lysine, Lys, K
- Arginine, Arg, R
- Histidine, His, H
Arg: The NH3+ group of Arg is very basic because its positive charge is stabilized by resonance.
His: The nitrogens of the cycle have a relatively weak affinity for an H+ and are only partly positive at neutral pH.
Uncharged polar side chains
Amino acids with uncharged polar side chains are relatively hydrophilic and are usually on the outside of proteins.
- Asparagine (Asn, N) and glutamine (Gln, Q): although the NH2 is not charged at neutral pH, it is polar.
- Serine (Ser, S), Threonine (Thr, T) and Tyrosine (Tyr, Y): the 'OH group is polar.
Nonpolar side chains
Amino acids with non polar side chains tend to cluster their side chains
together on the inside of proteins.
They are: G, P, A, V, L, I, F, M, W, C.
Paired cysteins allow disulphide bonds.



