Citing this page:
Lefranc, M.-P. and Lefranc, G.
Human Gm, Km and Am allotypes and their molecular characterization: a remarkable demonstration of polymorphism
In: B. Tait, F. Christiansen (Eds.), Immunogenetics,
chap. 34, Humana Press, Springer, New York, USA. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012; 882, 635-680. PMID: 22665258, LIGM: 406
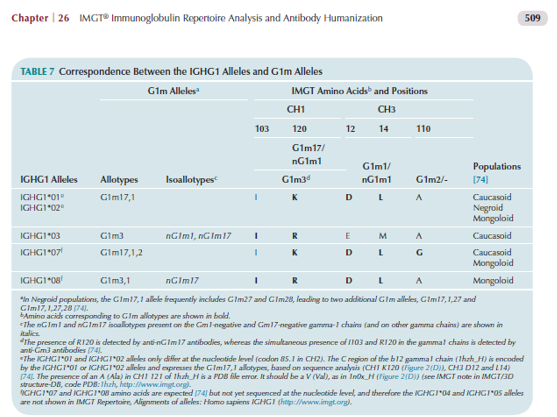
The G1m allotypes and alloallotypes define seven G1m alleles [6] which correspond to nine potential IGHG1 alleles (Table below).
The allotype G1m17 or G1m(z) corresponds to IGHG1 CH1 [Lys(K)120, a359] according to the IMGT unique numbering for C-DOMAIN [1]
(Exon numbering 97 [2], Eu numbering 214 [3]).
The allotype G1m17 (CH1 K120) (pale blue in the Table) is found on alleles IGHG1*01, IGHG1*02,
IGHG1*04, IGHG1*05, IGHG1*05p, IGHG1*06p and IGHG1*07p
[2,4,5,6].
The allotype G1m3 or G1m(f) corresponds to IGHG1 CH1 [Arg(R)120, g359]. For its expression, G1m3 is dependent on the presence of the IGHG1 CH1 isoleucine I103 [6].
The allotype G1m3 (R120 and I103) (blue in the Table) is found on alleles IGHG1*03 (G1m3 and nG1m1) and IGHG1*08p (G1m3,1) [4,5,6].
The Arg(R)120 is also found on IGHG3 and IGHG4 and is responsible of the isoallotype nG1m17 or nG1m(z) present on IGHG1 nG1m17 (IGHG1*03 G1m3 and IGHG1*08p G1m3,1), IGHG3 and IGHG4 [5,6].
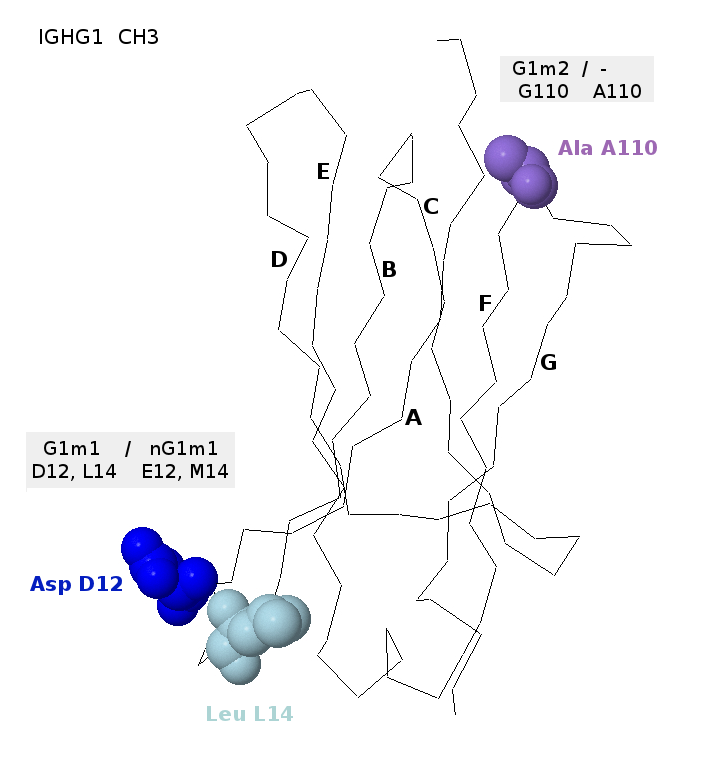
The allotype G1m1 or G1m(a) corresponds to IGHG1 CH3 [Asp(D)12, t36; Leu(L)14, c40] according to the
IMGT unique numbering for C-DOMAIN [1] (Exon numbering 16 and 18 [2],
Eu numbering 356 and 358 [3]).
The allotype G1m1 (CH3 D12, L14) (pale yellow in the Table) is found on alleles IGHG1*01,
IGHG1*02, IGHG1*04, IGHG1*05, IGHG1*05p
IGHG1*06p, IGHG1*07p and IGHG1*08p
[4,5,6].
The isoallotype nG1m1 or nG1m(a) corresponds to IGHG1 CH3 [Glu(E)12, g36; Met(M)14, a40].
The isoallotype nG1m1 (CH3 E12, M14) is found on allele IGHG1*03 [2,4,5,6]
and on IGHG2, IGHG3 and IGHG4 (only detected on H-gamma4 by certain antisera [6]).
The allotype G1m2 or G1m(x) corresponds to IGHG1 CH3 [Gly(G)110, g329] according to the IMGT unique
numbering for C-DOMAIN [1] (Exon numbering 91, Eu numbering 431 [3]).
The allotype G1m2 (purple in the Table) is found on allele IGHG1*07p (G. Lefranc and M.-P. Lefranc, personal communication and [6]).
The absence of the allotype G1m2 corresponds to IGHG1 CH3 [Ala(A)110, c329] which is found on alleles IGHG1*01, IGHG1*02, IGHG1*03, IGHG1*04, IGHG1*05, IGHG1*05p, IGHG1*06p and IGHG1*08p [4,5,6] and on IGHG2, IGHG3 and IGHG4. Ala(A)110 is not an isoallotype as no antibody reagent has been characterized [6].
Both Gm27 and Gm28 are qualified as "alloallotype", being an allotype for two different gamma chains, gamma1 (G1m27, G1m28) and gamma3 (G3m27, G3m28), depending on the populations [6].
The allotype G1m27 corresponds to IGHG1 CH3 [Ile(I)101, a301] according to the IMGT unique numbering for C-DOMAIN [1] (Exon numbering 82, Eu numbering 422 [3]).
The allotype G1m27 (green in the Table) is found on alleles IGHG1*04 and IGHG1*06p [6].
The allotype G1m28 corresponds to IGHG1 CH3 [Arg(R)115, g344; Tyr(Y)116] according to the IMGT unique numbering for C-DOMAIN [1] (Exon numbering 95 and 96, Eu numbering 435 and 436 [3]).
The allotype G1m28 (yellow in the Table) is found on alleles IGHG1*05p and IGHG1*06p [6].
IGHG1*01, IGHG1*02 and IGHG1*05 are G1m17,1 (previously written G1m1,17).
IGHG1*03 is G1m3 (previously written Gm3).
IGHG1*04 is G1m17,1,27 (1).
IGHG1*05p is G1m17,1,28.
IGHG1*06p is G1m17,1,27,28.
IGHG1*07p is G1m17,1,2 (previously written G1m1, 2, 17).
IGHG1*08p is G1m3,1.
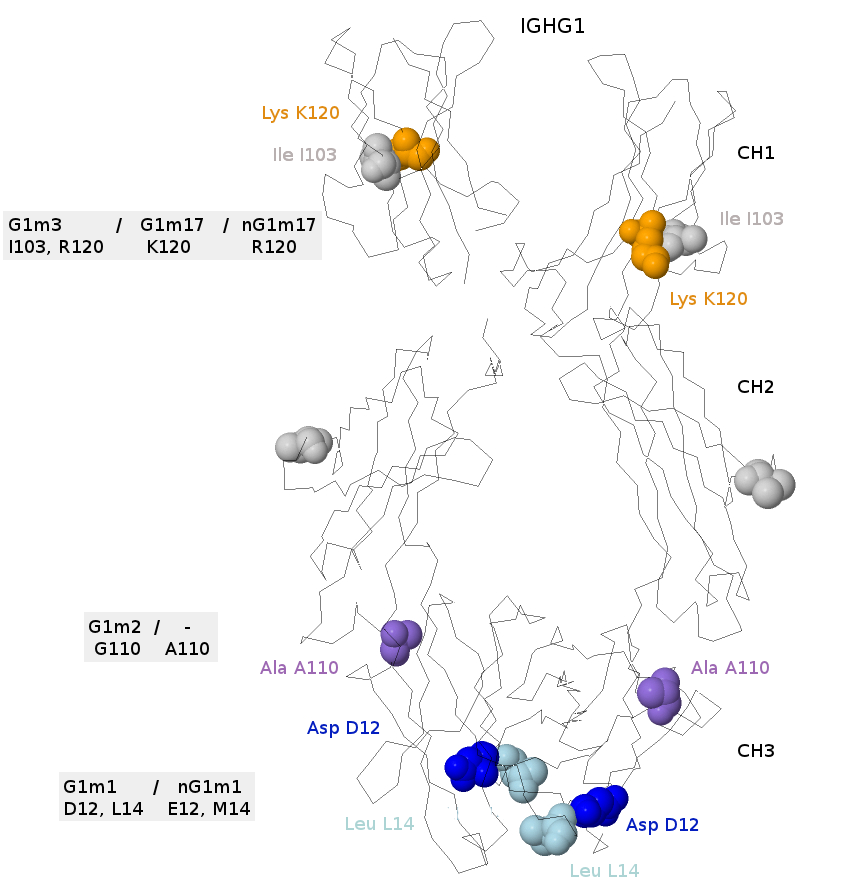
The CH1, CH2 and CH3 of the b12 gamma1 chains are shown (IMGT/3Dstructure-DB, code PDB:1hzh), with the positions involved in the G1m allotypes [6].
The CH2 position 45.1 is not related to the G1m allotypes, but indicates the amino acid position that should be responsible of the G2m23 allotype, or of its absence (G2m..), on a gamma2 chain [6].
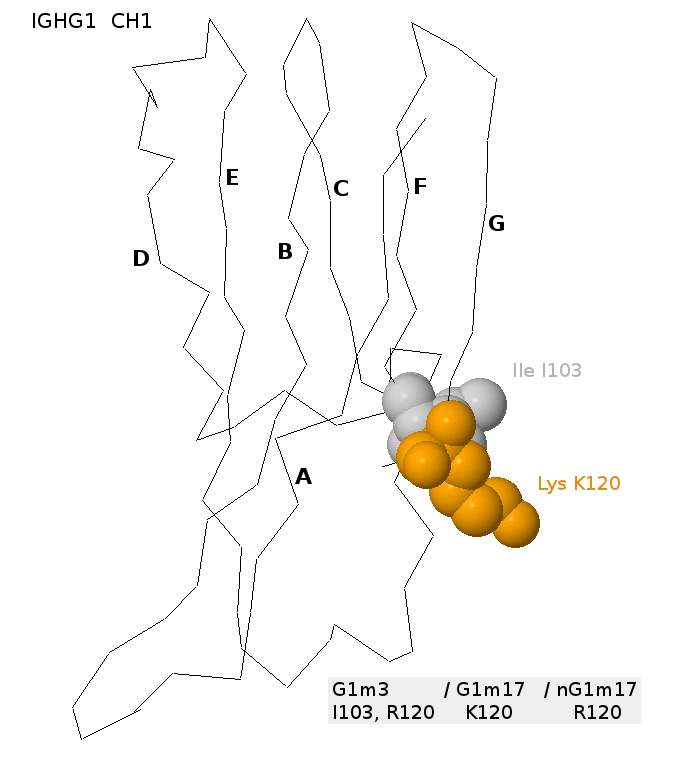
Three-dimensional structure of the IGHG1 CH1. The CH1 domain is from the b12 antibody (IMGT/3Dstructure-DB, code PDB:1hzh).
The lysine K120 (strand G) and the isoleucine I103 (strand F) are shown [6]. The K120 corresponds to the G1m17 allotype. The simultaneous presence of I103 (specific of the gamma1 isotype) and of arginine R120 would correspond to the G1m3 allotype.
The R120 would correspond to the nG1m17 isoallotype [6].
Three-dimensional structure of the IGHG1 CH3. The CH3 domain is from the b12 antibody (IMGT/3Dstructure-DB, code PDB:1hzh). Positions 12 and 14 of the G1m1/nG1m1 allotype, and position 110 of the G1m2/- allotype in the IGHG1 CH3 domain are shown [6].
The aspartate D12 and leucine L14 correspond to the G1m1 allotype, whereas alanine A110 corresponds to the absence of the G1m2 allotype. Glutamate E12 and and methionine M14 would correspond to nG1m1, whereas a glycine G110 would correspond to G1m2 [6].
| Amino acid positions (2) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH1 | CH3 | |||||||
| G1m alleles |
IGHG1 allele names (nt) |
120 | 12 | 14 | 101 | 110 | 115 | 116 |
| (97) | (16) | (18) | (82) | (91) | (95) | (96) | ||
| 214 | 356 | 358 | 422 | 431 | 435 | 436 | ||
| G1m17,1 | IGHG1*01 IGHG1*02 IGHG1*05 |
K120 (G1m17) |
D12, L14 (G1m1) |
|||||
| K Lys aaa |
D Asp gat |
L Leu ctg |
V Val gtc |
A Ala gct |
H His cac |
Y Tyr tac |
||
| G1m3 | IGHG1*03 | R120 with I103 (G1m3) R120 (nG1m17) |
E12, M14 (nG1m1) |
|||||
| R Arg aga |
E Glu gag |
M Met atg |
V Val gtc |
A Ala gct |
H His cac |
Y Tyr tac |
||
| G1m17,1,27 | IGHG1*04 (1) | K120 (G1m17) |
D12, L14 (G1m1) |
I101 (G1m27) |
||||
| K Lys aaa |
D Asp gat |
L Leu ctg |
I Ile atc |
A Ala gct |
H His cac |
Y Tyr tac |
||
| G1m17,1,28 | IGHG1*05p (3) | K120 (G1m17) |
D12, L14 (G1m1) |
R115, Y116 (G1m28) |
||||
| K (Lys) aaa |
D (Asp) gat |
L (Leu) ctg |
V Val gtc |
A (Ala) gct |
R (Arg) (cgc) |
Y Tyr tac |
||
| G1m17,1,27,28 | IGHG1*06p (3) | K120 (G1m17) |
D12, L14 (G1m1) |
I101 (G1m27) |
R115, Y116 (G1m28) |
|||
| K (Lys) aaa |
D (Asp) gat |
L (Leu) ctg |
I (Ile) atc |
A (Ala) gct |
R (Arg) cgc |
Y (Tyr) tac |
||
| G1m17,1,2 | IGHG1*07p (3) | K120 (G1m17) |
D12, L14 (G1m1) |
G110 (G1m2) |
||||
| K (Lys) (aaa) |
D (Asp) (gat) |
L (Leu) (ctg) |
V Val gtc |
G Gly (ggt) |
H His (cac) |
T Tyr (tac) |
||
| G1m3,1 | IGHG1*08p (3) | R120 with I103 (G1m3) R120 (nG1m17) |
D12, L14 (G1m1) |
|||||
| R (Arg) aga |
D (Asp) (gat) |
L (Leu) (ctg) |
V Val gtc |
A (Ala) (gct) |
H His (cac) |
Y (Tyr) (tac) |
||
| (1) | IGHG1*04 differs from the alleles IGHG1*01, IGHG1*02 and IGHG1*05 by the amino acid change V101>I which corresponds to the allotype Gm27 [6], IGHG1*04 is therefore G1m17,1,27. |
| (2) | Amino acid numbering in bold is according to IMGT unique numbering for C-DOMAIN [1], between parentheses: exon numbering [2] and in italics: Eu numbering [3]. |
| (3) | IGHG1*05p, IGHG1*06p, IGHG1*07p and IGHG1*08p amino acid and codon between parentheses are expected (G. Lefranc and M.-P. Lefranc) [2,5,6] but not yet sequenced at the nucleotide level and therefore the IGHG1*05p, IGHG1*06p, IGHG1*07p and IGHG1*08p alleles are not shown in Alignments of alleles: IGHG1. The alleles IGHG1*05p (G1m17,1,28), IGHG1*06p (G1m17,1,27,28), IGHG1*07p (G1m17,1,2) and IGHG1*08p (G1m3,1), described in Lefranc and Lefranc [6] (Table 4, p649), will be assigned with a definitive allele number (based on a chronological basis, and therefore unrelated to the provisional 'p' number) when a complete genomic sequence will be available. |
| [1] | Lefranc, M.-P. et al., Dev. Comp. Immunol., 29, 185-203 (2005).
PMID: 15572068
|
| [2] | Lefranc G. and Lefranc M.-P. The Immunoglobulin FactsBook, Academic press, London, UK, 458 pages (2001). |
| [3] | Correspondence between C numberings (in IMGT Scientific chart). |
| [4] | Alignment of alleles: Human IGHG1 (in IMGT Repertoire). |
| [5] | Lefranc G. PhD Thesis. Allotypes et haplotypes des immunoglobulines dans les communautés libanaises: intérêt exceptionnel en immunogénétique et séro-anthropologie (in French). Immunoglobulin allotypes and haplotypes in the Lebanese communities : discussion of unusual genetic events and population structure (in English) Université de Rouen (1978). |
| [6] | Lefranc, M.-P. and Lefranc, G. Human Gm, Km and Am allotypes and their molecular characterization: a remarkable demonstration of polymorphism In: B. Tait, F. Christiansen (Eds.), Immunogenetics, chap. 34, Humana Press, Springer, New York, USA. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012; 882, 635-680. PMID: 22665258, LIGM: 406 |
Excerpt of:
Lefranc M-P. IMGT® immunoglobulin repertoire analysis and antibody humanization.
In: Alt, F.W, Honjo, T, Radbruch A. and Reth, M. (Eds.), Molecular Biology of B cells, Second edition, Academic Press, Elsevier Ltd, London, UK, Chapter 26, 2014, PP. 481-514.
dx.doi.org, ISBN : 978-0-12-397933-9. LIGM: 438
page 508-509 (source above to be quoted)
Allotypes are polymorphic markers of an IG subclass that correspond to amino acid changes and are detected serologically by antibody reagents (74). In therapeutic antibodies (human, humanized or chimeric) (11), allotypes may represent potential immunogenic residues (73), as demonstrated by the presence of antibodies in individuals immunized against these allotypes (74). The allotypes of the human heavy gamma chains of the IgG are designated as Gm (for gamma marker). The allotypes G1m, G2m and G3m are carried by the constant region of the gamma1, gamma2 and gamma3 chains, encoded by the IGHG1, IGHG2 and IGHG3 genes, respectively (74). The gamma1 chains may express four G1m alleles (combinations of G1m allotypes): G1m3, G1m3,1, G1m17,1, and G1m17,1,2 (and in Negroid populations two additional G1m alleles, Gm17,1,28 and Gm17,1,27,28) (74) (Table 7). The C region of the G1m3,1, G1m17,1 and G1m17,1,2 chains differ from that of the G1m3 chains by two, three and four amino acids, respectively (74). The correspondence between the G1m alleles and IGHG1 alleles is shown in Table 7. Thus, IGHG1*01 and IGHG1*02 are G1m17,1, IGHG1*03 is G1m3, IGHG1*04 is G1m17,1,2 and IGHG1*05 is G1m3,1. In the IGHG1 CH1, the lysine at position 120 (K120) in strand G corresponds to the G1m17 allotype (74) (Figure 2D and Figure 5B). The isoleucine I103 (strand F) is specific of the gamma1 chain isotype. If an arginine is expressed at position 120 (R120), the simultaneous presence of R120 and I103 corresponds to the expression of the G1m3 allotype (74). For the gamma3 and gamma4 isotypes (which also have R120 but T in 103), R120 only corresponds to the expression of the nG1m17 isoallotype (an isoallotype or nGm is detected by antibody reagents that identify this marker as an allotype in one IgG subclass and as an isotype for other subclasses) (74). In the IGHG1 CH3, the aspartate D12 and leucine L14 (strand A) correspond to G1m1, whereas glutamate E12 and methionine M14 correspond to the nG1m1 isoallotype (74) (Table 7). A glycine at position 110 corresponds to G1m2, whereas an alanine does not correspond to any allotype (G1m2-negative chain) (Table 7). Therapeutic antibodies are most frequently of the IgG1 isotype, and to avoid a potential immunogenicity, the constant region of the gamma1 chains are often engineered to replace the G1m3 allotype by the less immunogenic G1m17 (CH1 R120>K) (G1m17 is more extensively found in different populations) (74).
| [11] | Poiron, C. , Wu, Y., Ginestoux, C., Ehrenmann, F., Duroux, P., and Lefranc, M.-P. (2010). IMGT/mAb-DB: the IMGT® database for therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. 11èmes Journées Ouvertes de Biologie, Informatique et Mathématiques (JOBIM), Montpellier, 7-9 September 2010. |
| [73] | Jefferis, R., and Lefranc, M.-P (2009). Human immunoglobulin allotypes: Possible implications for immunogenicity. MAbs 1(4), 332-338. |
| [74] | Lefranc, M.-P., and Lefranc, G. (2012). Human Gm, Km and Am allotypes and their molecular characterization: a remarkable demonstration of polymorphism. In Immunogenetics (F. Christiansen and B. Tait, Eds.), Chap. 34. Humana Press, Springer, New York. Methods Mol Biol. 882, 635-680. |



© Copyright 1995-2025 IMGT®, the international ImMunoGeneTics information system® | Terms of use | About us | Contact us | Citing IMGT